Honda
SAVS Project
Designing a new seating experience for a shared autonomous vehicule.

Summary
This research was conducted by a team of designers and engineers from The Ohio State University as part of the Shared Autonomous Vehicle Seat (SAVS) research project sponsored by Honda R&D Americas. The main objective of this project was to develop a new car seat that Honda could use in its future self-service Level 4 autonomous vehicles. To achieve this objective, five main tasks were carried out. First, a market research was conducted on Level 4 autonomous vehicles. Second, a business model that fits with the new autonomous vehicle was created. Third, the ergonomics and the placement of the seats were defined. Fourth, prototypes, 3D models and renderings of the vehicle seats and interior were designed. Finally, usage scenarios were developed to explain the experience of the service, the use of the vehicle, and the seats and their maintenance.
My Role
Managing the team, developing user scenarios, conducting market and field researches, leading codesign activities, designing prototypes (mock‑ups, wireframes, 3D models), testing ergonomics, writing reports, presenting to the clients
Tools
Axure, Photoshop, Illustrator, InDesign, Codesign maketools, Solidworks, Google Workspace
Research
The first goal of the research phase of this project was to become familiar with the different types and levels of autonomous vehicles. Secondly, its goal was to understand the current market for car-sharing vehicles, and finally to conduct a short survey to validate the future appeal of autonomous shared vehicles among 18-34-year-olds.
Level 4 Autonomous Vehicle
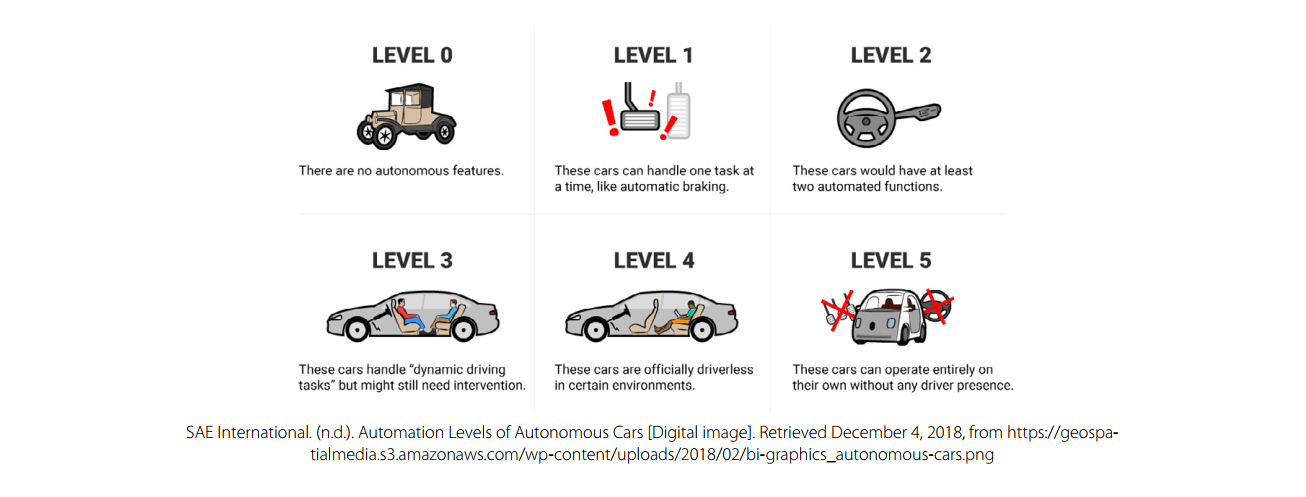
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) scale for autonomous vehicles has six levels. Level 0 has no autonomous features at all, and Level 5 vehicles are fully autonomous. In this project, the team was tasked with developing new seating for level 4 autonomous vehicles. These are vehicles that are normally driven in a fully autonomous way, while still allowing a user to temporarily take control and drive in certain specific situations.
Survey
As part of the research process, a survey was deployed to allow the team to get an idea of the social climate towards shared autonomous vehicles and to validate some of the team’s design assumptions. The survey helped to illuminate respondents' comfort level with using an autonomous self-service car service, in what context they would want to use this type of service, and how they would spend their time during the commute.
Business Model Development
In order to design seating for the vehicle, it was essential to understand the context in which the seating would be used. A business model for the autonomous sharable vehicle therefore had to be developed.
Exploration of the Solution Space
In order to not exclude any possible solutions, we had to define the solution space of our problem. After the research phase of our project, we were able to create a matrix of three axes to create this solution space. Within these three axes, we were able to classify the existing business models of the different shared vehicle companies.
The three axes that we developed were the following:
- A social versus an individual commuting experience.
- A vehicle based on comfort versus a work efficiency context.
- A vehicle made for a short commute versus a long commute.
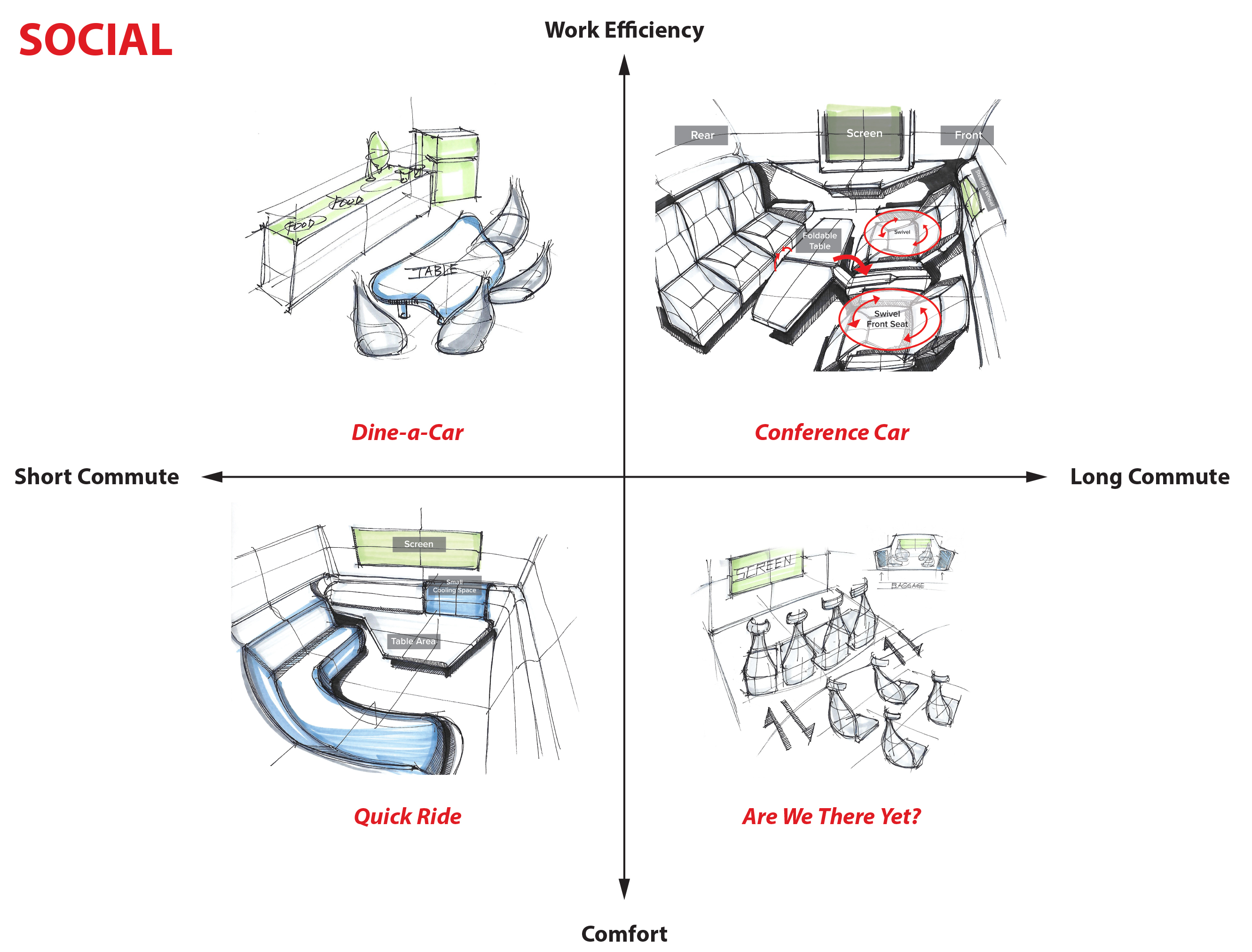
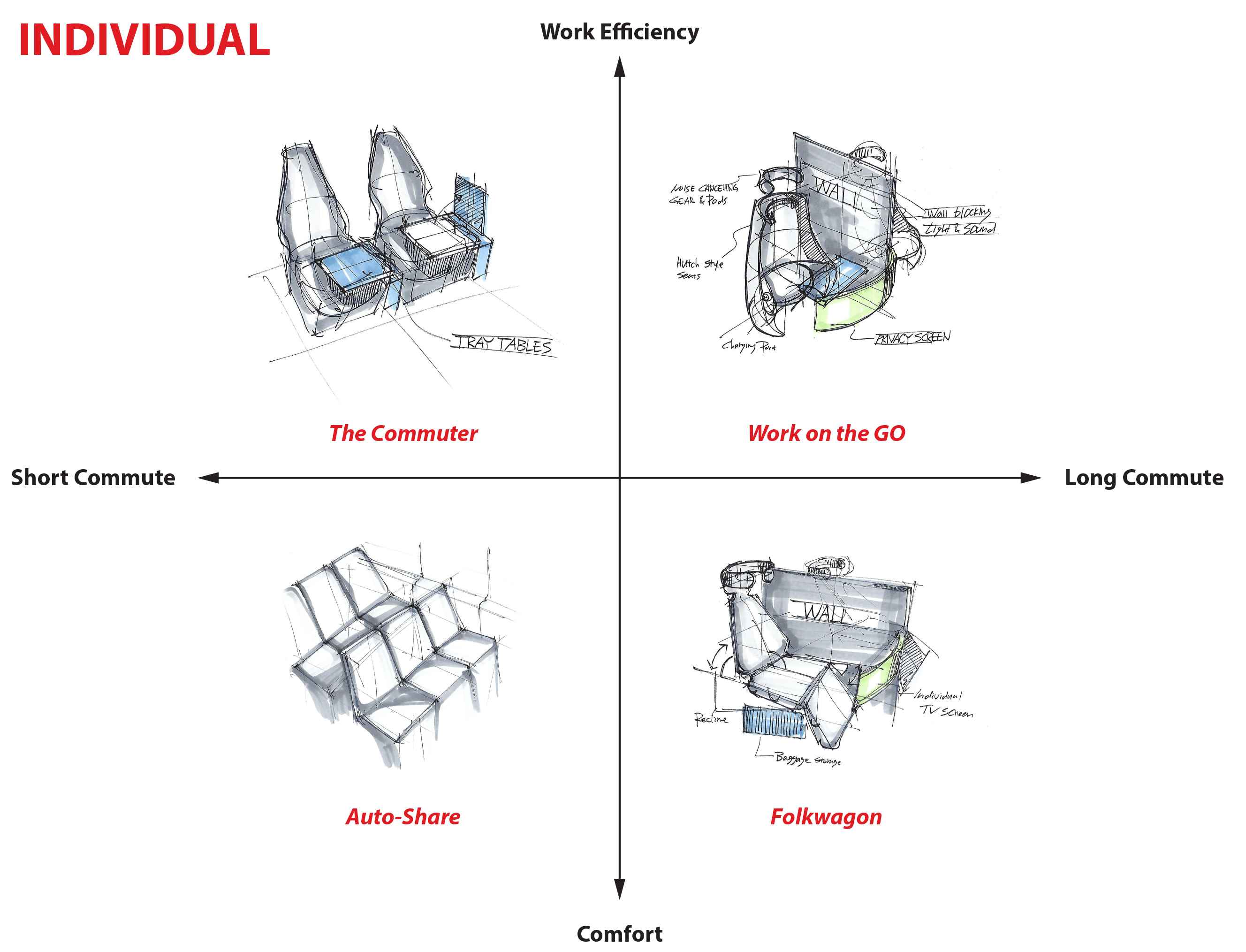 In the end, and after discussions with the client, the team opted for a business model that favored a more social experience where trips would average from 30 minutes to about 3 hours. The vehicle would allow for both relaxation and work depending on the user's preferences.
In the end, and after discussions with the client, the team opted for a business model that favored a more social experience where trips would average from 30 minutes to about 3 hours. The vehicle would allow for both relaxation and work depending on the user's preferences.
Prototyping
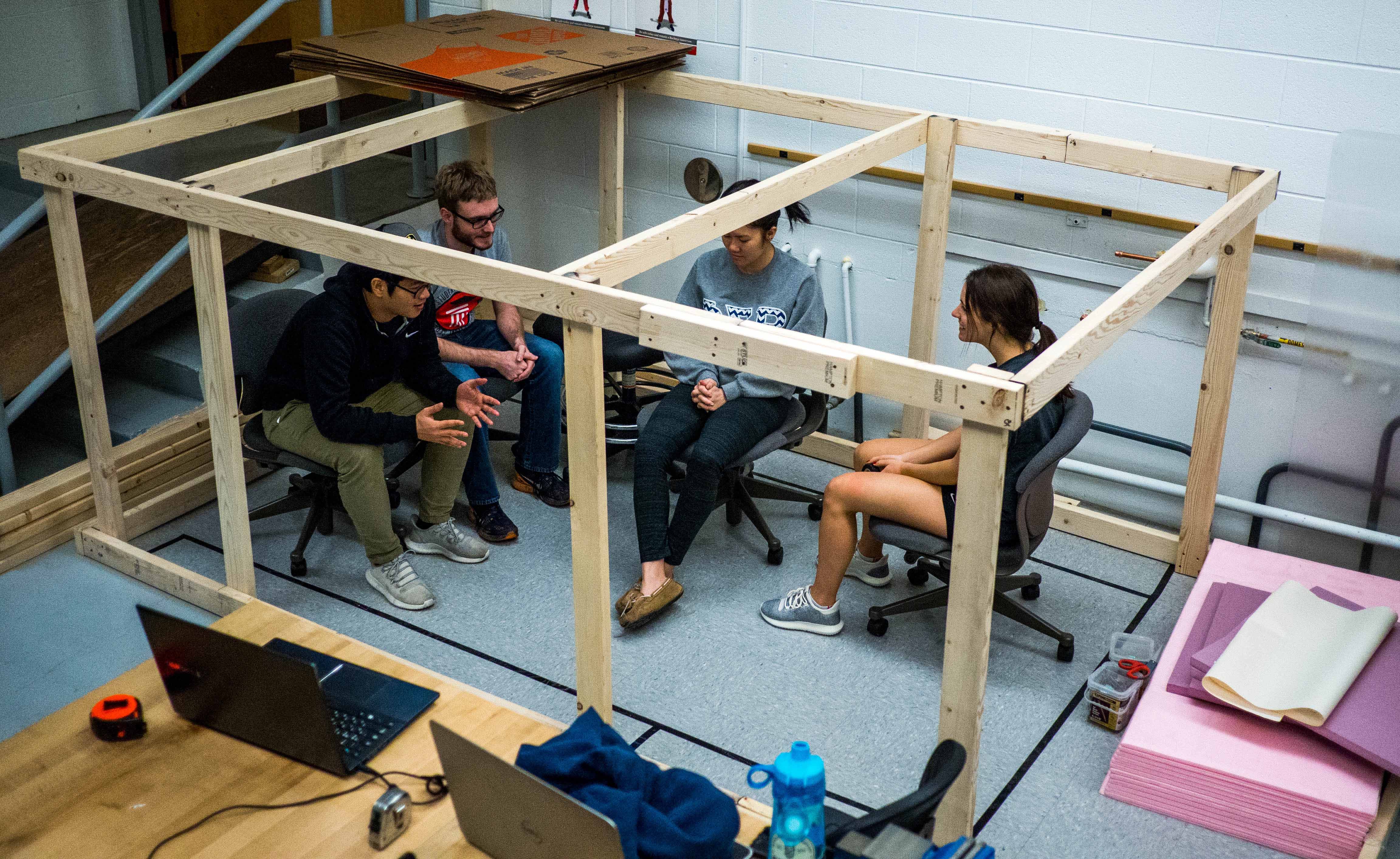 The seat prototyping was based on the dimensions of a 2019 Honda Pilot. After test driving the vehicle and becoming more familiar with its dimensions, the team built a volume model to be able to test configurations for the interior and its ergonomics at a 1:1 scale.
The seat prototyping was based on the dimensions of a 2019 Honda Pilot. After test driving the vehicle and becoming more familiar with its dimensions, the team built a volume model to be able to test configurations for the interior and its ergonomics at a 1:1 scale.
Seat Configuration
The mock-up was used to test different cockpit configurations to find the one that would best fit the business model criteria while favoring the passengers' comfort. Following these tests, the team concluded that an L-shaped configuration with a pivoting driver's seat would be best suited.
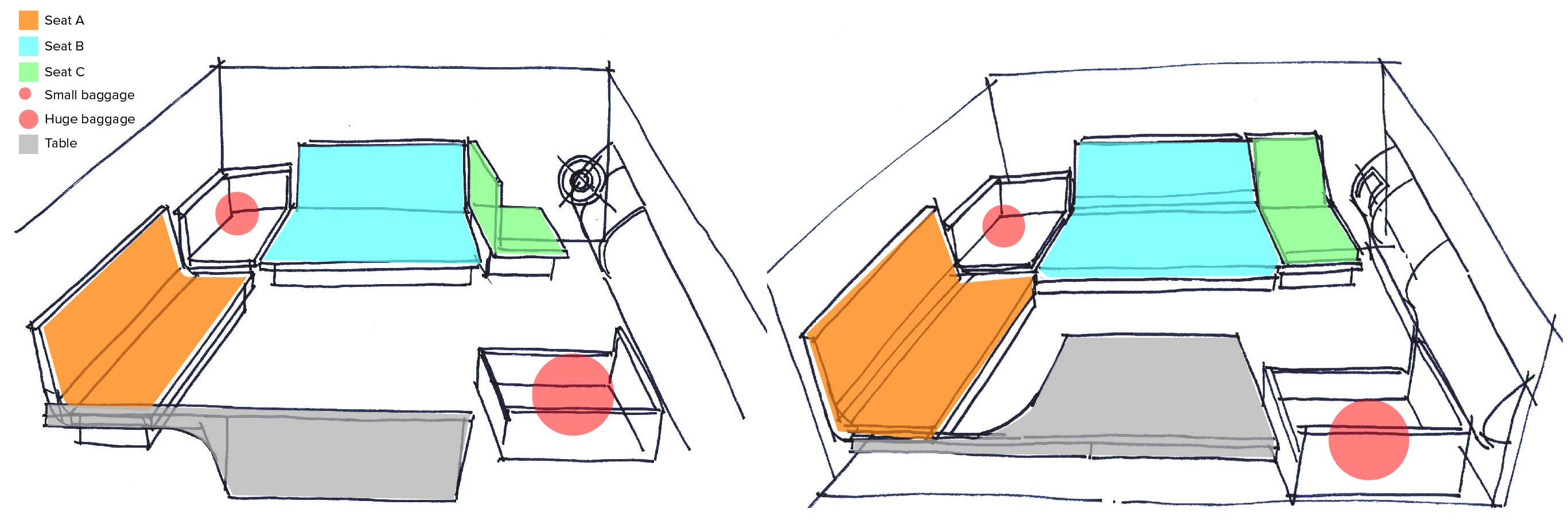
Seat design
Several iterations and mock-ups were also produced for the actual seat design. These mock-ups were used to test the different characteristics of the seat, the materials used and its features. In addition, the seat was also tested with users for periods of 30 minutes to 1 hour to evaluate its comfort and improve its design.

Final Design
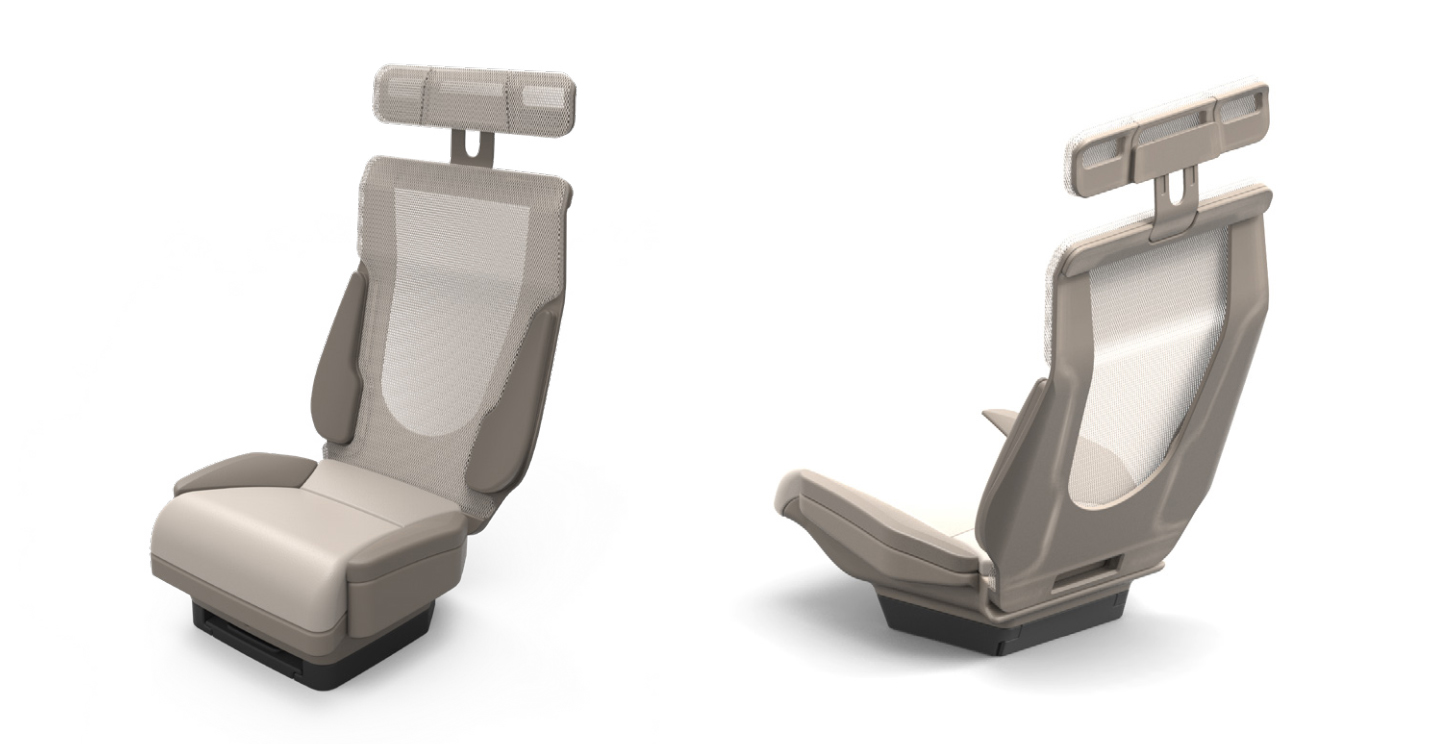 The Honda Shared Autonomous Vehicle (SAV) Experience is a car-sharing service managed by a private company. Using electric autonomous level 4 vehicles, the cars can transport up to four passengers completely independently in most scenarios. The service is optimized to facilitate the movement of its users in urban areas and between cities within a maximum radius of approximately 3 hours driving-time. It is therefore well suited to serve both a professional clientele and to help travel with family or friends.
The Honda Shared Autonomous Vehicle (SAV) Experience is a car-sharing service managed by a private company. Using electric autonomous level 4 vehicles, the cars can transport up to four passengers completely independently in most scenarios. The service is optimized to facilitate the movement of its users in urban areas and between cities within a maximum radius of approximately 3 hours driving-time. It is therefore well suited to serve both a professional clientele and to help travel with family or friends.
7 Unique Features
The final seat concept represents a combination of seven unique features. Each of these features is intended to optimize both the operation of the shared autonomous vehicle service, and the user experience within the previously described business model.
1. Four Seats, One Design
The first key feature is that all four seats in the vehicle share one common design. This greatly reduces manufacturing costs and simplifies maintenance. If any seat in the vehicle gets damaged, it can be replaced quickly.
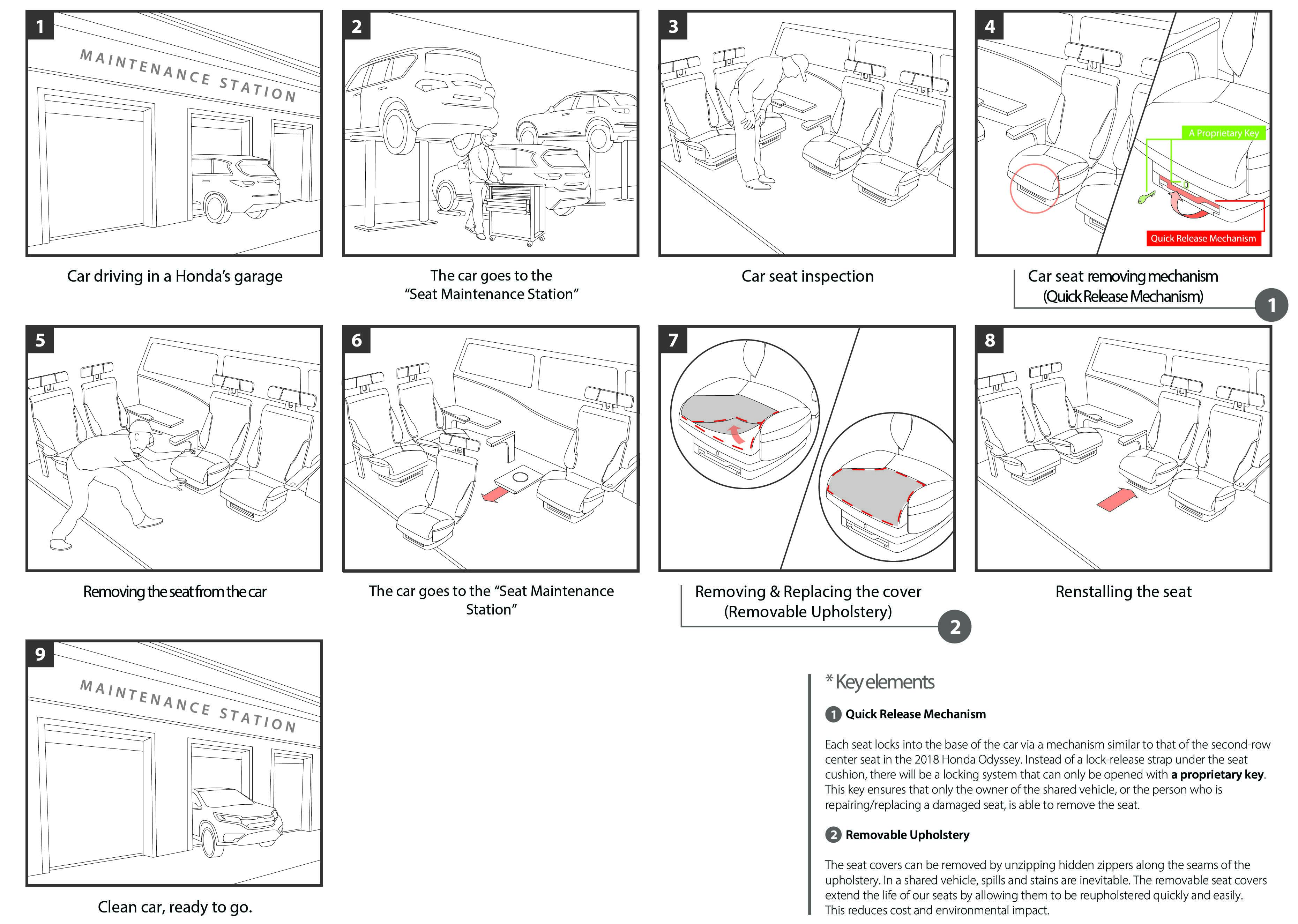
2. Quick-Release Mechanism
The second key feature is the seat base’s utilization of the quick release technology currently available in the Honda Odyssey. Originally used for the Odyssey’s 2nd row middle seat, the technology has been repurposed to allow easy removal and reinstallation of the seats during maintenance.
 3. Swivel Front Seat
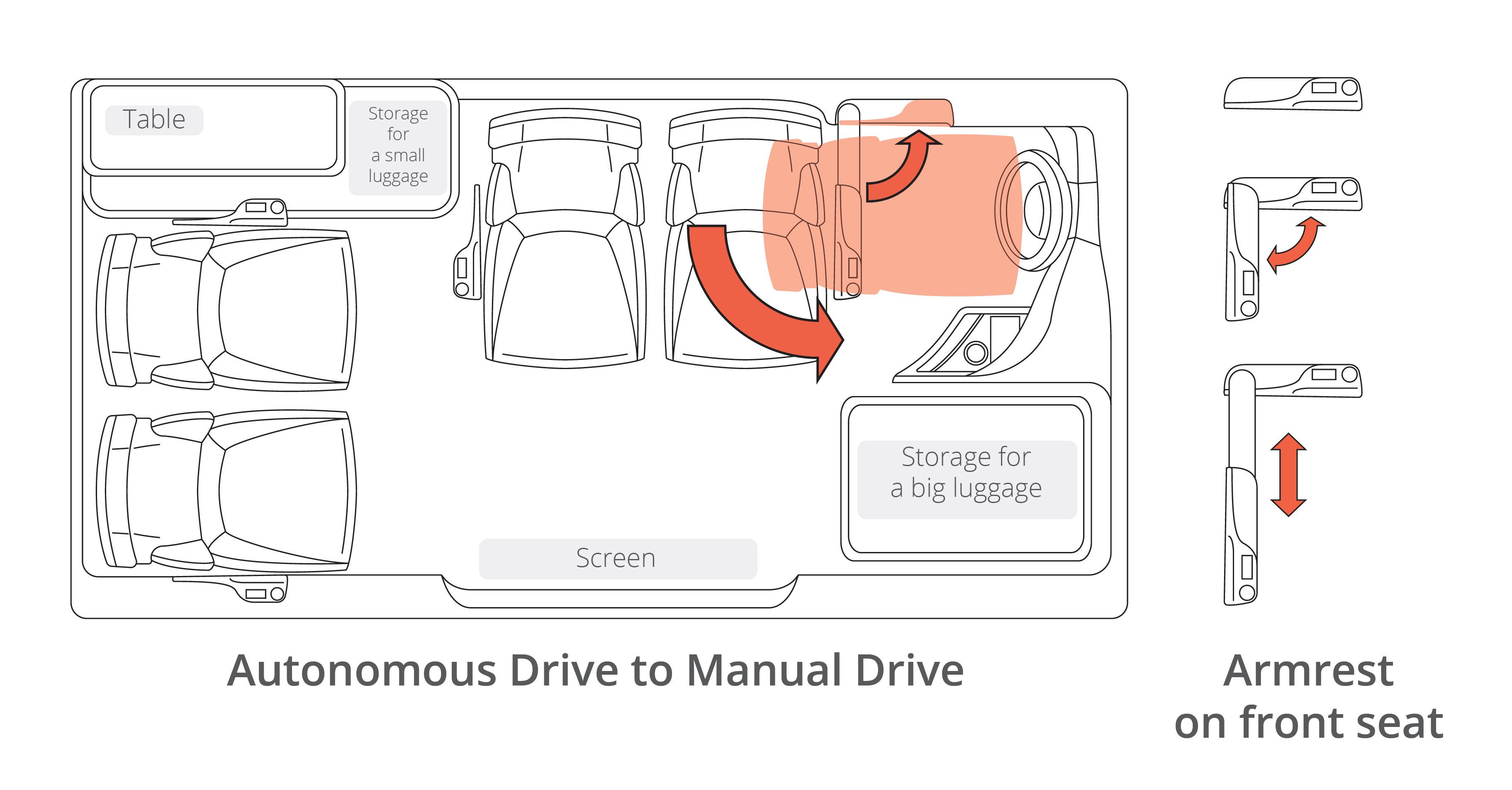
3. Swivel Front Seat
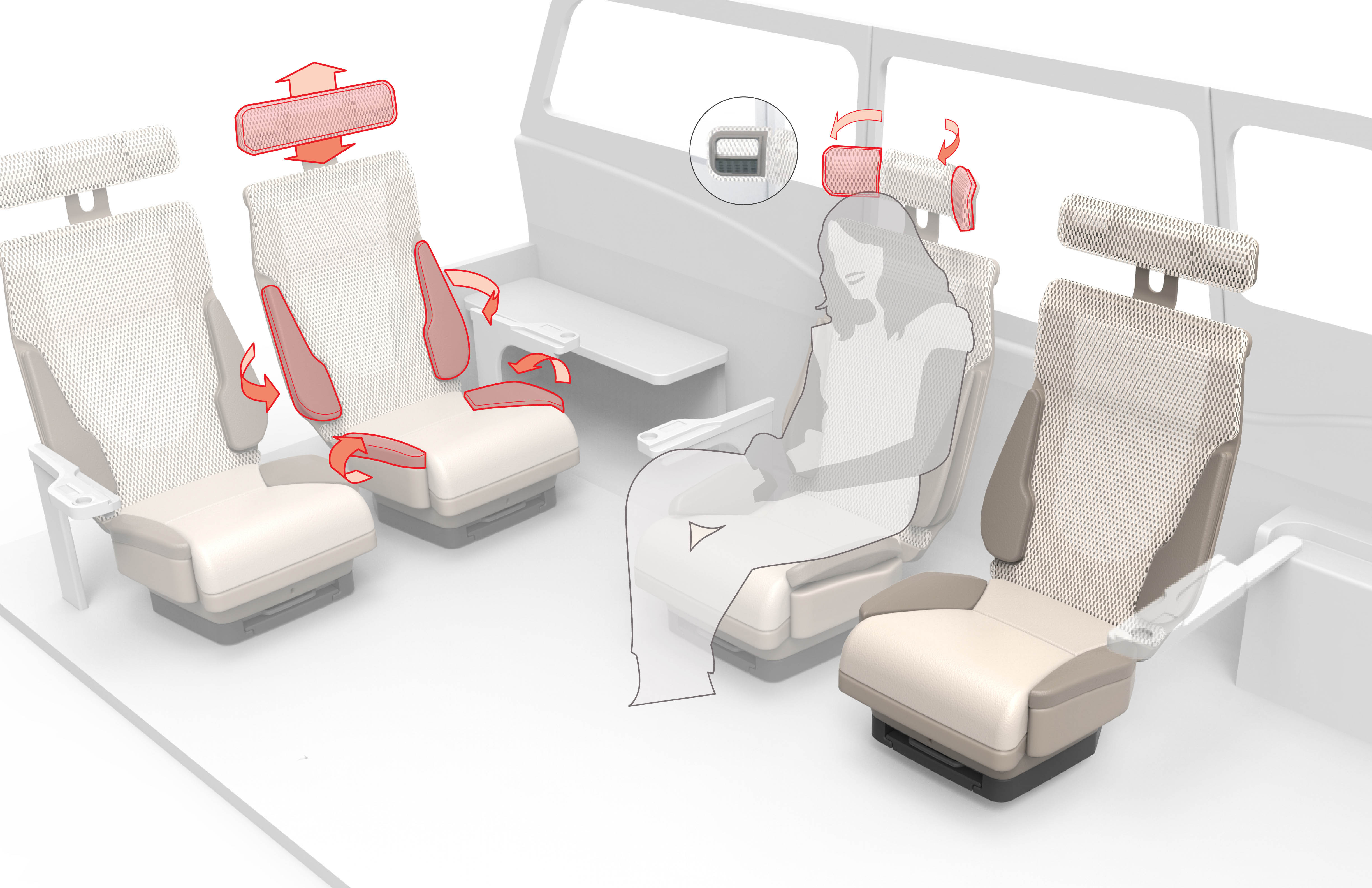
The third key feature is the ability of the driver’s seat to rotate 90 degrees clockwise from the conventional driving position to face inwards while the vehicle is in autonomous mode. This allows the seat to smoothly transition to a more relaxed social position, and ensures an equal riding experience for the driver.
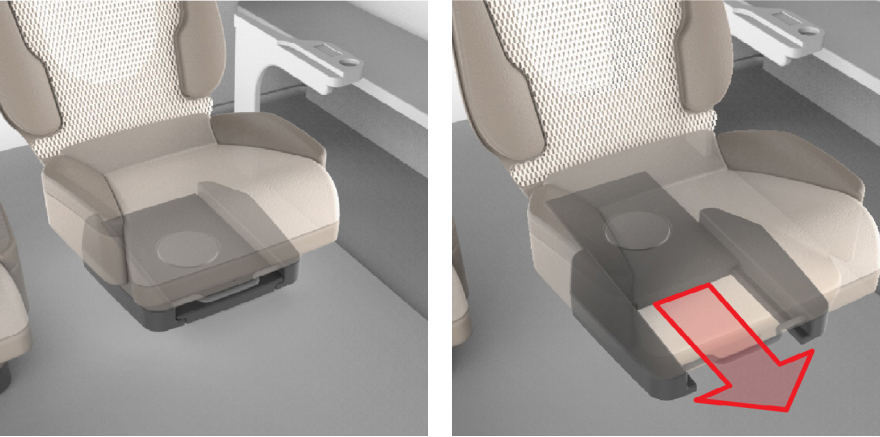
 4. Adjustable Bolsters and Headrest
4. Adjustable Bolsters and Headrest
The fourth key feature is the ability of the bottom bolsters, side bolsters, and sides of the headrest to rotate through 45 degrees of adjustment. This offers a higher level of individual customization for users and improves the seat’s ability to adapt to different body shapes and user activities.
 5. Contoured Seat Edge
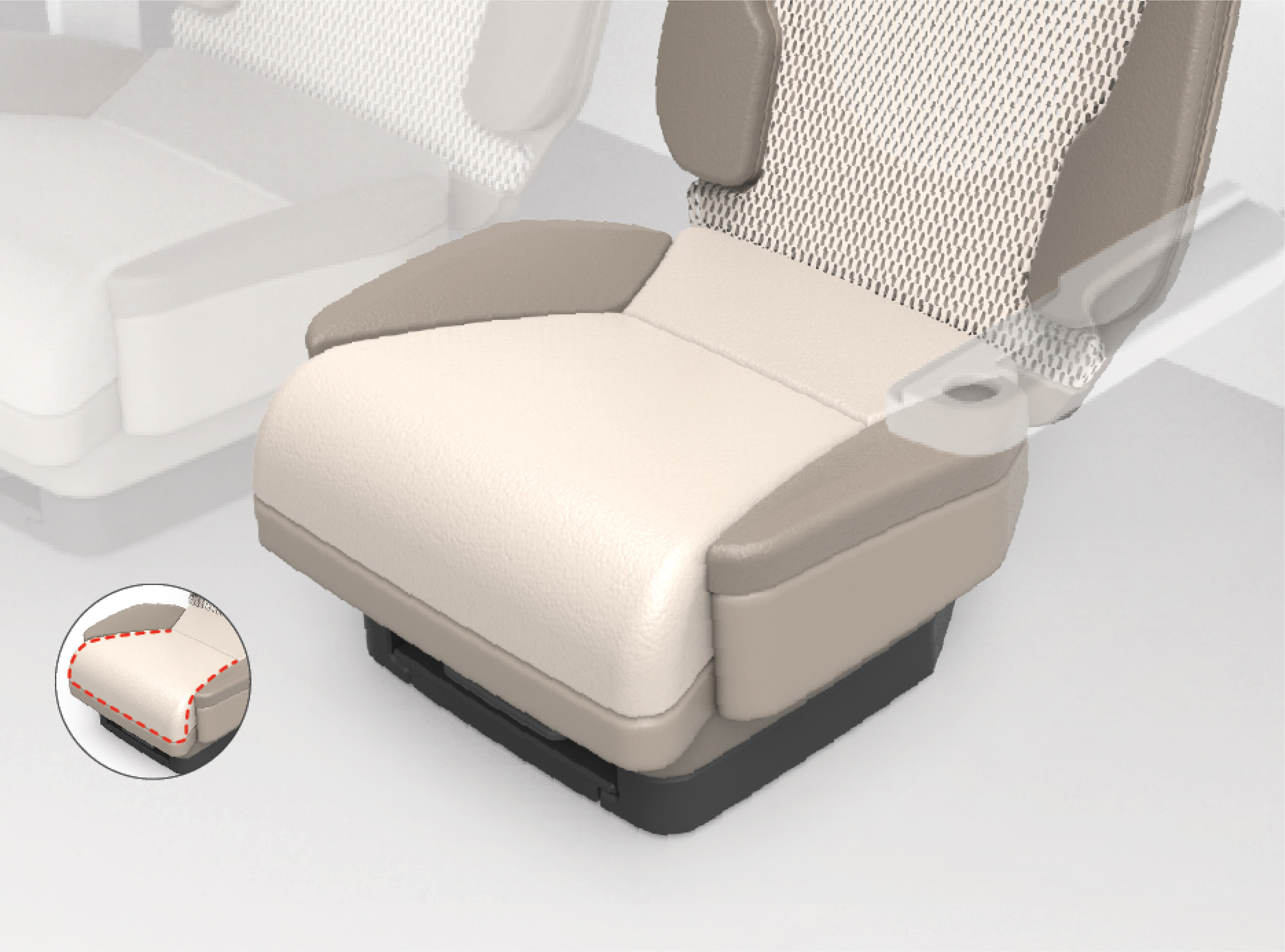
5. Contoured Seat Edge
The fifth key feature is unique convex contour of the front edge of the seat inspired by lounge furniture, instead of the typical flat or concave seat edge required for driving. The convex shape guides the user’s body to slide farther back into the seat, into a more relaxed and supported position.
6. Mesh Backing and Supracor Base
The sixth key feature is a combination of two strategic material selections to make the seat more lightweight while retaining or even improving comfort. Mesh material was inlaid on the back of the seat, which eliminated the need for heating and cooling fixtures. Supracor, a lightweight plastic mesh, was placed on the base of the seat for continual comfort.
 7. Removable Upholstery
7. Removable Upholstery
The seventh and final key feature is the separation of the seat’s upholstery into individual parts that can be removed and replaced using a hidden zipper on the edge of the material. This allows for easy cleaning and repair of the upholstery. This will also help to reduce downtime during the maintenance of the car seat and improve the sustainability of the seats.
User Scenarios
In conjunction with the design of the new SAVS features, the team developed four user scenarios to better explain them and how the user would interact with the autonomous vehicle. These scenarios also explain how the service operates and overview the maintenance of the seats.
First-time & Frequent Users Scenario
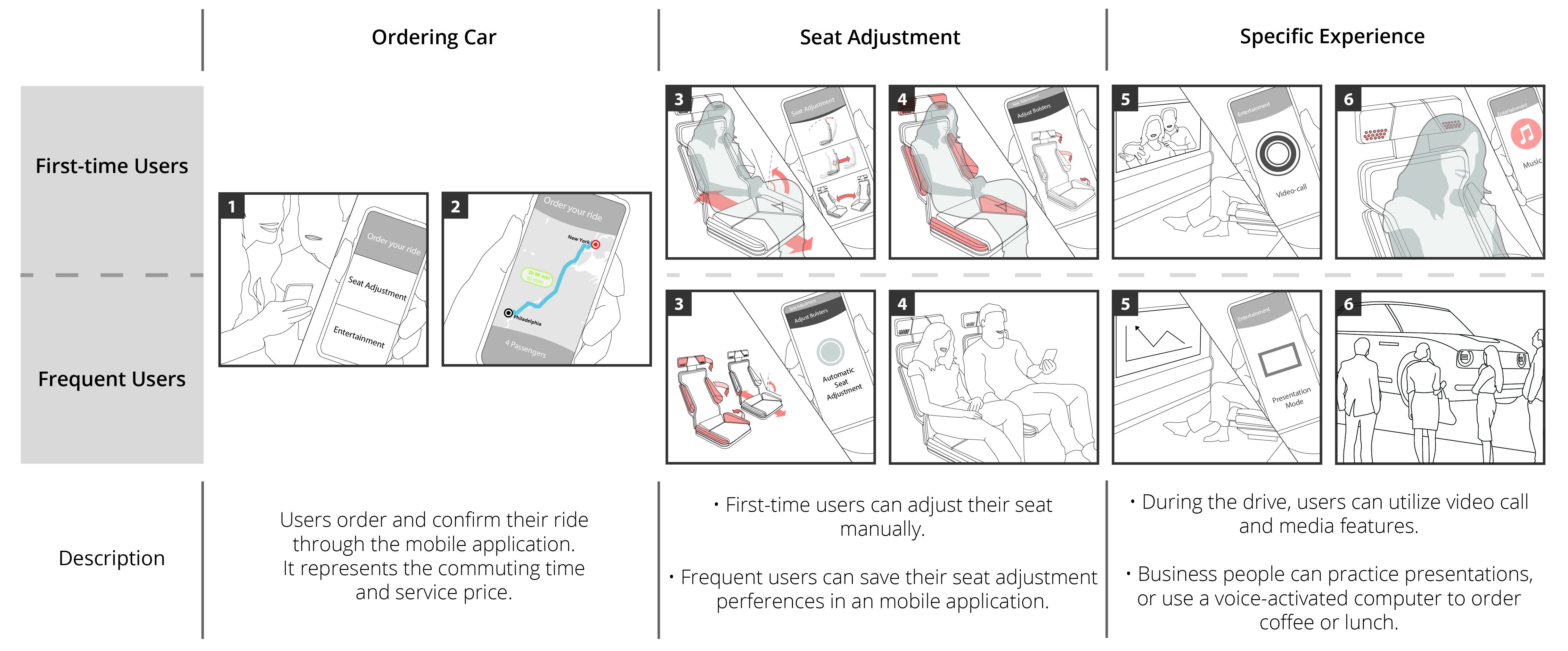
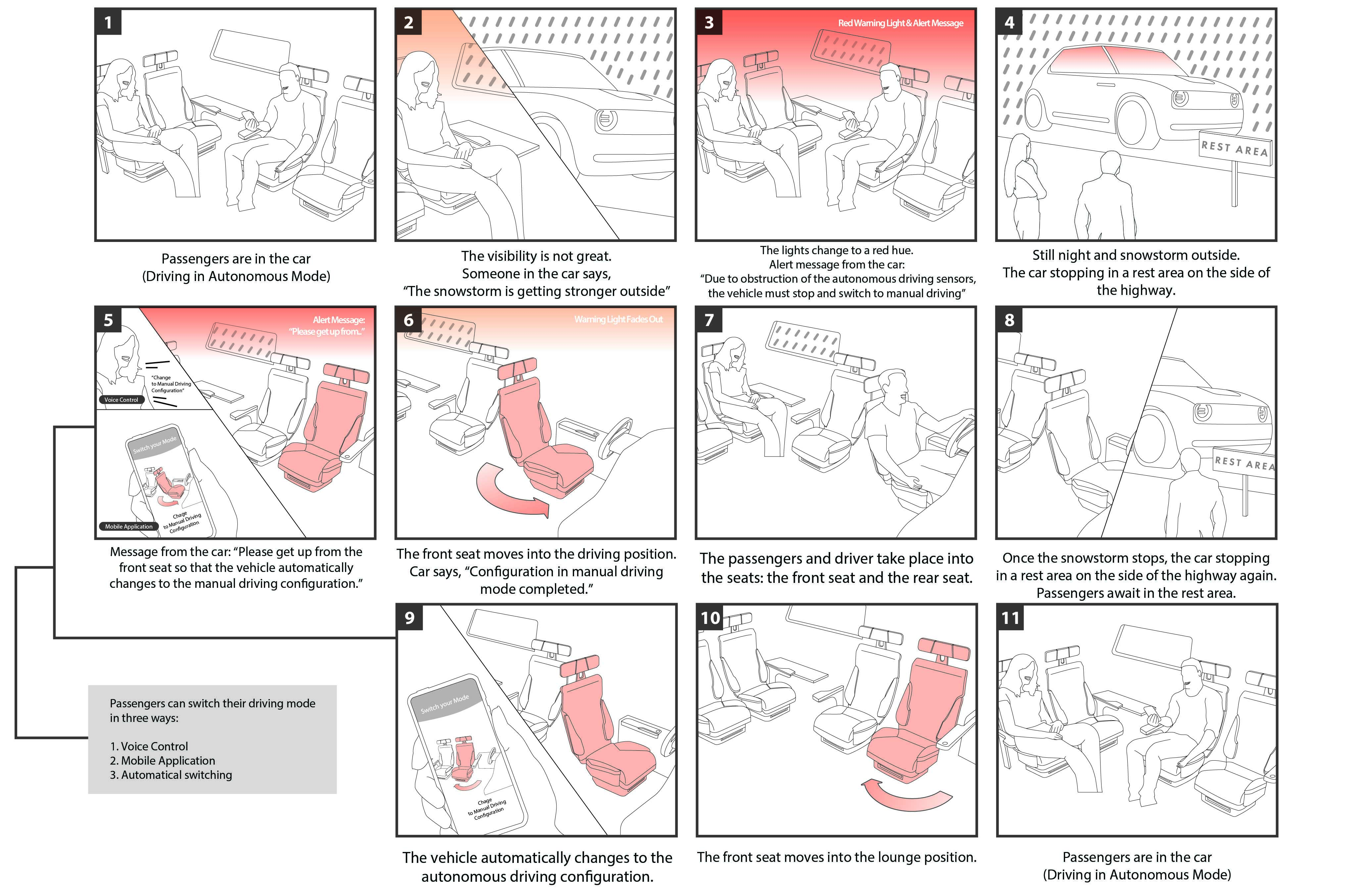
Switch to Manual Driving Mode Scenario
Car maintenance scenario